EV Test Functions
|

|
Visual checking
|

|
Insulation & Equalization Test
|

|
BMS Charging Test
|
|
Whether below items has any visual damage
Charging Part & Socket;
Instrumentation & Signal Indicators;
Power Battery;
Wiring Harness & High-voltage Components;
|
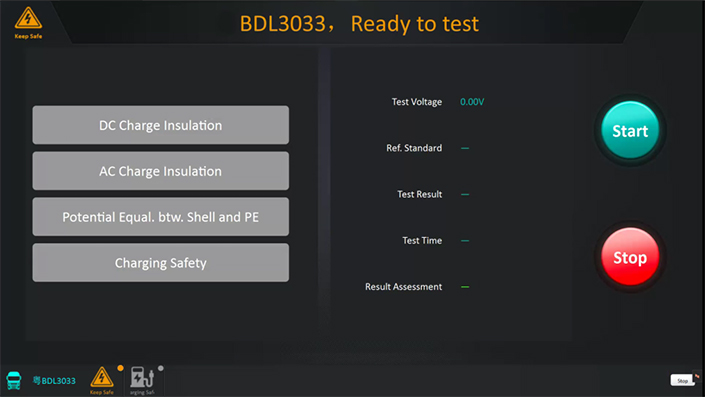
DC Charge Insulation;
AC Charge Insulation;
Potential Equalization Between Shell & E Platform;
Potential Equalization Between Shells;
|
State of Charge;
Max. Temperature of Battery;
Max. Voltage of Secondary Cell;
Charging Simulation for State of Health;
|

|
ECU Dis-charging Test
|

|
BMS Dis-charging Monitoring
|

|
Dis-Charging Simulation
|
|
Real-time monitoring of the performance via EV-OBD
Driving Motor Temperature;
Motor Controller Temperature;
DC/Dc Converter Temperature;
|
Real-time monitoring of the performance via EV-OBD
Max.Temperature of Battery;
Min.Voltage of Secondary Cell;
|
Driving at 0~130km/h on the 4WD chassis dyno;
Test the basic stability of driving;
EV Electromagnetic radiation Test;
|
Background
According to the requirements of China's National New Energy Vehicle Development Plan(2021-2035), Electric Vehicle becomes the main part of Automobile industry. To ensure on-road safety, charging safety, and driver safety with electric vehicles, in-use electric vehicles should be tested and evaluated using effective and pragmatic methods.
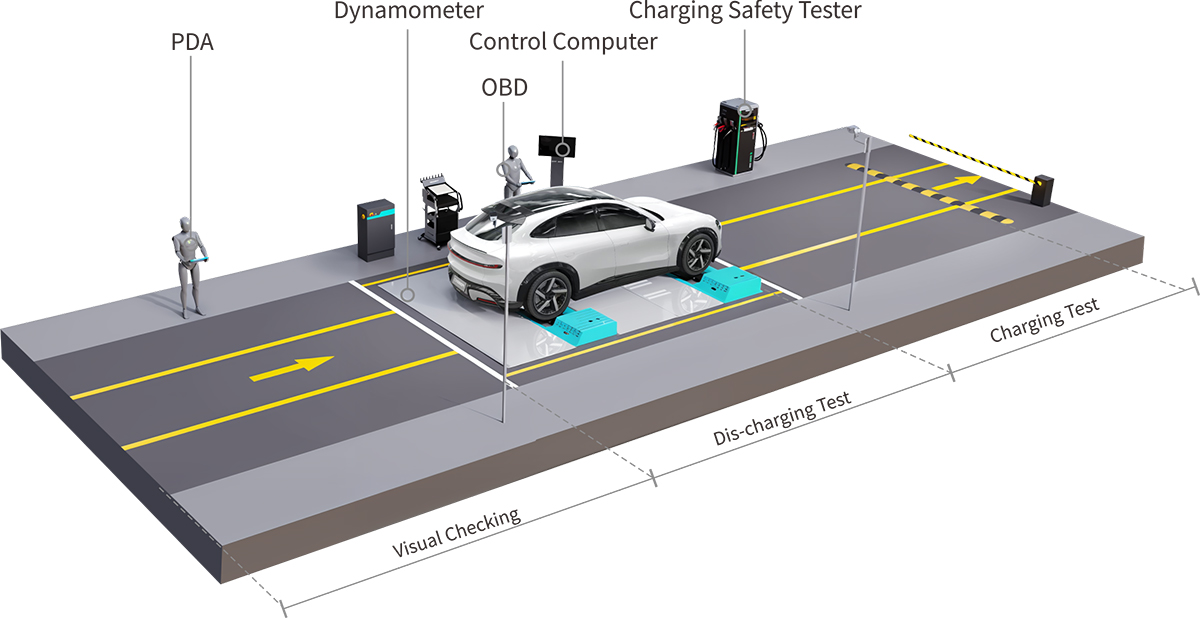
Video: The Process of EV Test Solution
Test Process
The solution encompasses two core parts: charging detection and discharging detection. Charging detection, also referred to as static detection, primarily assesses the performance of potential equalization and the insulation resistance of the charging port. Discharging detection, known as dynamic detection, mainly evaluates the safety of the power battery, the drive motor, and the electronic control system.

SL
|
|
Test Item
|
Value
|
Standard
|
Result
|
|
Test ltem : Power Battery Safety
|
|
1
|
Charging
|
Max. Temperature of 8 attery
|
31
|
≤60℃
|
PASS
|
|
2
|
Max, Voltage of Secondary Cell
|
374
|
≤4.5V
|
PASS
|
|
3
|
Secondary CellValtage Range
|
000
|
≤0.3V
|
PASS
|
|
4
|
Discharging
|
Max.Temperature of Battery
|
31
|
≤65℃
|
PASS
|
|
5
|
Min.Voltage of Secondary Cel
|
352
|
>1.8V
|
PASS
|
Test Item:Driving Motor Safety
|
|
6
|
Driving Motor Temperature
|
600
|
≤175℃
|
PASS
|
|
7
|
Motor Controller Temperature
|
550
|
≤95℃
|
PASS
|
|
Test Item:Electrical Control System Safety
|
8
|
DC/DC Converter Temperature
|
400
|
≤95℃
|
PASS
|
Test Item :Electrical Safety
|
|
9
|
DC Charge Insulation
|
4515014.6
|
≥100Ω/V
|
PASS
|
|
10
|
AC Charge Insulation
|
1096.5
|
≥1MQΩ
|
PASS
|
|
11
|
Poterntial Equalization Between Shell&E Platform
|
0.07
|
≤0.10Ω
|
PASS
|
|
12
|
PentialEqualization Between Shells
|
0.02
|
≤0.20Ω
|
PASS
|
|
Remark:This is the screen shot of actual test report based on China technical regulation, and it shall be different case by case due to the different regulation and technical condition.
|
Core Configuration
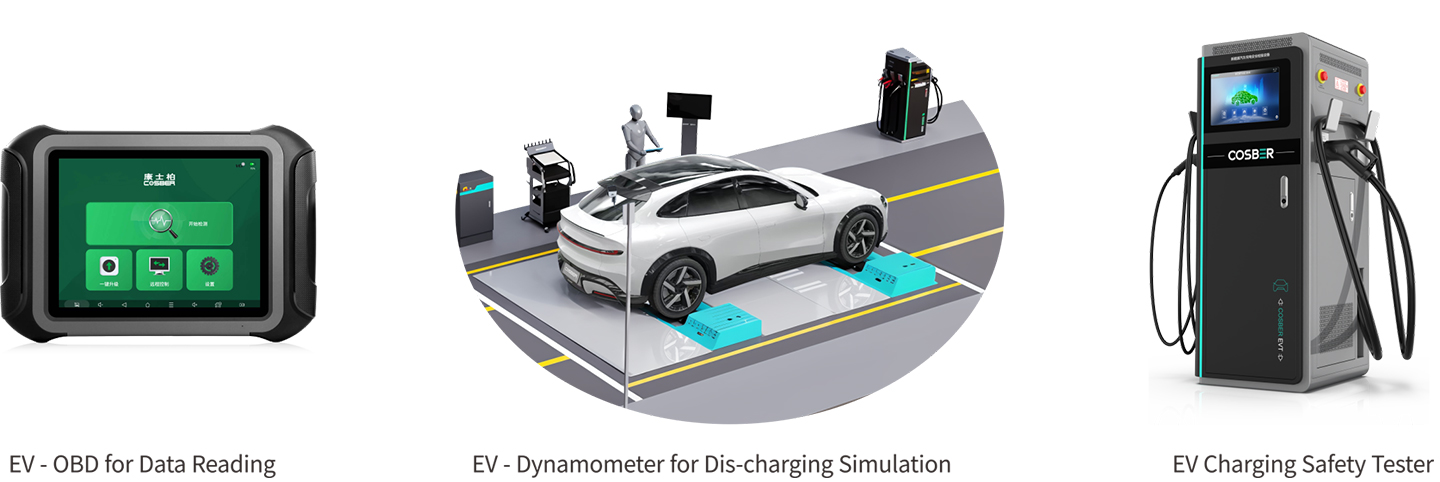
EV Charging Safety Tester(CCS-2 type)
Introducing the Cosber’s EV Charging Safety Tester, designed for electric vehicles with European CCS-2 charging standards. This advanced equipment offers comprehensive testing and monitoring capabilities, including high voltage insulation checks, potential equalization assessments, and BMS communication analysis. Additionally, it functions as an AC/DC EV charger, providing versatility and convenience in one device.
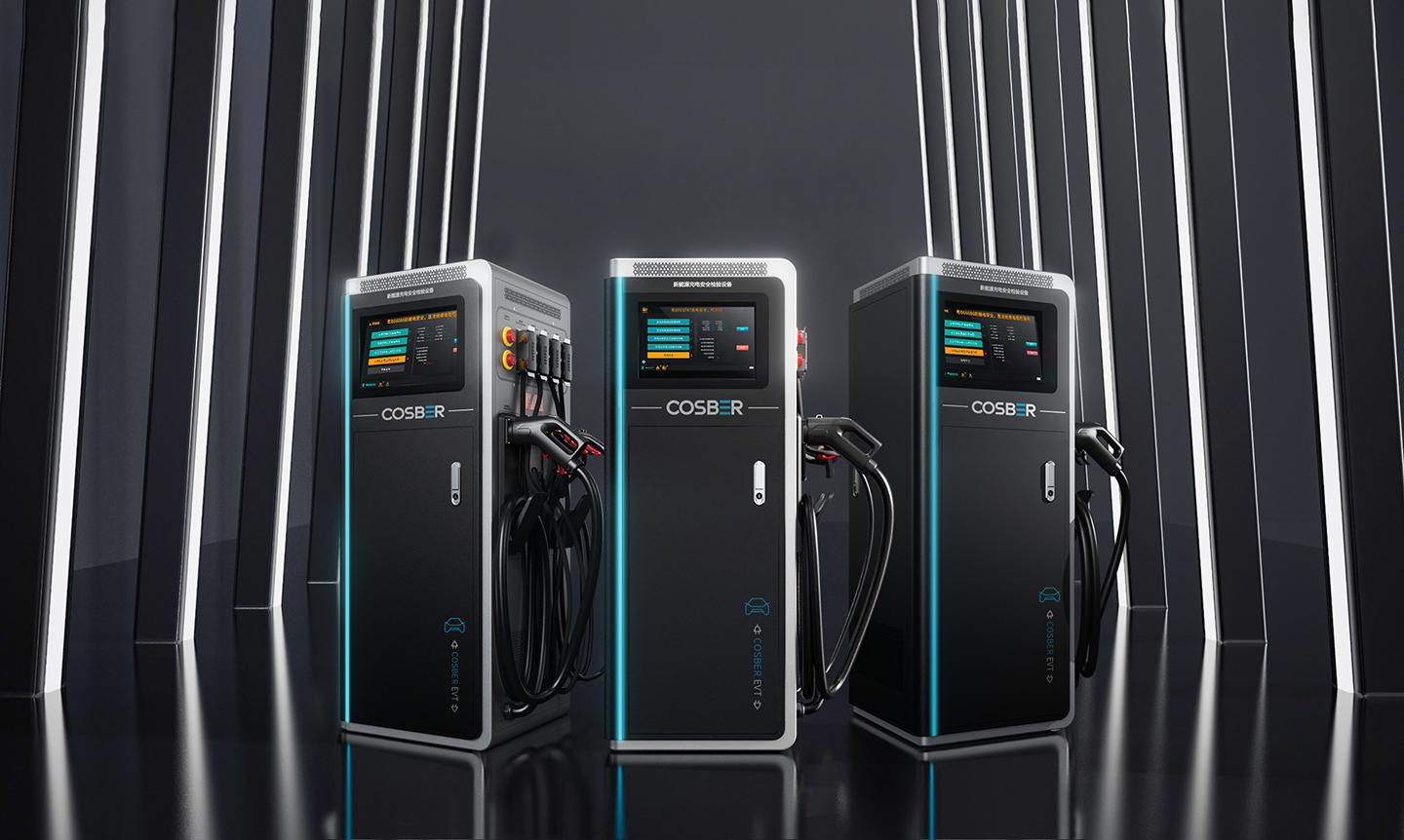

Detection Function
|
Test Function
|
Value Range
|
Standard
|
|
SOH
|
0-100%
|
≥70%
|
|
DC Charge Insulation
|
0-2000KΩ/V
|
≥100Ω/V
|
|
AC Charge Insulation
|
0.1-1000MΩ
|
≥1MΩ
|
|
Potential Equal. btw. EV and P.E
|
0.01-20Ω
|
≤0.1Ω
|
|
CCS-2 type DC charging capacity
|
0-30kW
|
|
Equipment Parameter
Operational Power
|
AC 380V+10%,50/60HZ+5%
|
|
No-Load/Full Load Power Consumption
|
0.2/30kW
|
|
Operational Environment
|
Temperature:0~40?°C;Humidity:20~90%RH
|
|
Dimension(WLH)
|
600×600×1600mm
|
|
Equipment Weight
|
150Kg
|
Dynamometer for EV
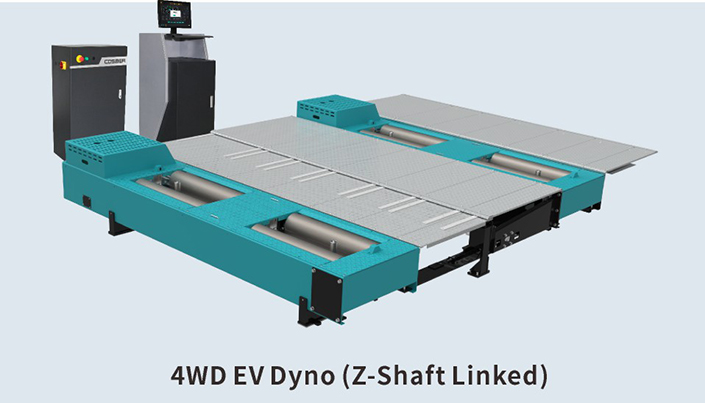
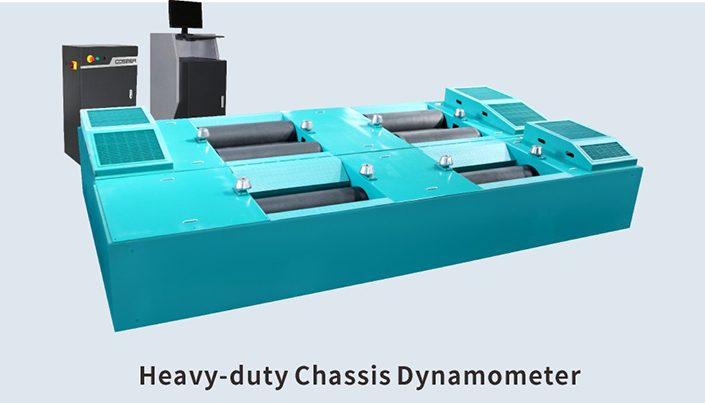
Dyno Bench Technical Data
|
Item
|
4WD EV Dyno(Z-Shaft Linked)
|
Heavy-duty chassis Dyno
|
|
Maximum carrying vehicle mass
|
5000kg
|
-
|
|
Maximum bearing axle mass
|
3000kg
|
13000kg
|
|
Maximum absorption driving force
|
0〜6000N×2
|
0-10000 N
|
|
Max. test speed
|
130 km/h
|
130 km/h
|
|
Roller diamete
|
Ф216mm
|
Ф373mm
|
|
Roller length
|
1000mm
|
1050mm
|
|
Inside wheel thread
|
700mm
|
900mm
|
|
Outer wheel thread
|
2700mm
|
2900mm
|
|
Minimum vehicle wheelbase
|
2300mm
|
-
|
|
Maximum vehicle wheelbase
|
3300mm
|
-
|
|
Eddy current rated power
|
160 kw x 2
|
700 kW(max absorbtion power)
|
|
Back drag motor power
|
7.5kW
|
11 kw(transducer control)
|
Software UI

|

|
|
Dis-charging/Charging Test Software
|
Dis-charging Test Interface
|
|
|
|
Charging Test Interface
|
EV Test Operation Info. System
|
General Q&A
Q: Is the OBD device available for any EV mode?
A: No, OBD is based on whether the OBD protocol of the EV, and without it, OBD can not be programmed and used.
Q: What is the use of the OBD?
A: It is used to read the data from the MCU&ECU via OBD port during the dis-charging test.
Q: Why the dynamometer is necessary in the solution?
A: To do the dis-charging test, it is important to make the actual driving simulation.